
Introduction to Ansible :-
Ansible is an agent-less IT automation tool developed in 2012 by Michael DeHaan, a former Red Hat associate. The Ansible design goals are : minimal, consistent, secure, highly reliable, and easy to learn.Ansible is Written on Python language.It also available as Open Source.
Why to use Ansible as automation tool ?
- There are many other IT automation tools available, including more mature ones like Puppet and Chef, so why would we choose Ansible? The main reason is simplicity.
- Ansible is using YAML syntax. It’s simple configuration language.
Puppet and Chef are using Ruby Syntax. which is more difficult to learn. - Ansible is an agentless tool.Instead of install an agent on every target machine, Ansible just requires that target systems have Python (on Linux servers) or PowerShell (on Windows servers) and SSH.But puppet and chef have to install agent on each target machines.
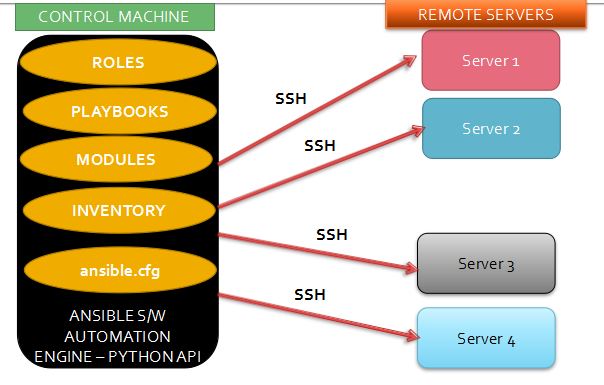
High Level Steps : –
- Install Python software
- Install PIP to install Cx_Oracle package to perform SQL commands
- Install ansible rpm
- Configure SSH to connect remote hosts
- Run the ansible command to access remote hosts.
Step 1:- Check the Current version of Python in OEL 7:-
[root@ansible ~]$ python -V Python 2.7.5
Note:- Minimum version of python 2.7.6 is needed to install ansible.
Step 2:- Download the Python 2.7.6 package
[root@ansible ansible]# wget -c https://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.7.6/Python-2.7.6.tgz --no-check-certificate --2018-07-19 02:16:25-- https://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.7.6/Python-2.7.6.tgz Resolving www.python.org (www.python.org)... 151.101.184.223, 2a04:4e42:2c::223 Connecting to www.python.org (www.python.org)|151.101.184.223|:443... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 14725931 (14M) [application/octet-stream] Saving to: ‘Python-2.7.6.tgz’ 100%[============================================================================================================>] 14,725,931 240KB/s in 65s 2018-07-19 02:17:32 (221 KB/s) - ‘Python-2.7.6.tgz’ saved [14725931/14725931]
Step 3:- Unzip the downloaded python package
[root@ansible ~]$ tar -xvzf Python-2.7.6.tgz [root@ansible ~]$ cd Python-2.7.6 [ansible@ansible Python-2.7.6]$ ls -lrt total 956 -rw-r--r--. 1 ansible ansible 12749 Nov 10 2013 LICENSE drwxr-xr-x. 2 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Include drwxr-xr-x. 2 ansible ansible 20 Nov 10 2013 Grammar drwxr-xr-x. 22 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Demo drwxr-xr-x. 46 ansible ansible 8192 Nov 10 2013 Lib drwxr-xr-x. 22 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Tools -rw-r--r--. 1 ansible ansible 97308 Nov 10 2013 setup.py drwxr-xr-x. 5 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 RISCOS -rw-r--r--. 1 ansible ansible 53972 Nov 10 2013 README drwxr-xr-x. 2 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Python -rw-r--r--. 1 ansible ansible 34829 Nov 10 2013 pyconfig.h.in drwxr-xr-x. 2 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 PCbuild drwxr-xr-x. 10 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 PC drwxr-xr-x. 2 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Parser drwxr-xr-x. 3 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Objects drwxr-xr-x. 9 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Modules drwxr-xr-x. 5 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Misc -rw-r--r--. 1 ansible ansible 44172 Nov 10 2013 Makefile.pre.in drwxr-xr-x. 11 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Mac -rwxr-xr-x. 1 ansible ansible 7122 Nov 10 2013 install-sh -rw-r--r--. 1 ansible ansible 133573 Nov 10 2013 configure.ac -rwxr-xr-x. 1 ansible ansible 426595 Nov 10 2013 configure -rwxr-xr-x. 1 ansible ansible 35639 Nov 10 2013 config.sub -rwxr-xr-x. 1 ansible ansible 44851 Nov 10 2013 config.guess drwxr-xr-x. 16 ansible ansible 4096 Nov 10 2013 Doc
Step 4:- Configuring python 2.7.6 software
Create the below directory ‘/home/ansible/python’ and configure,install the software.
[ansible@ansible Python-2.7.6]# ./configure --prefix=/home/ansible/python [ansible@ansible Python-2.7.6]# make [ansible@ansible Python-2.7.6]# make install
After installation,the following files are created under ‘/home/ansible/python’
[ansible@ansible Python-2.7.6]# ls -lrt /home/ansible/python total 4 drwxr-xr-x. 3 ansible ansible 22 Jul 19 21:10 include drwxr-xr-x. 4 ansible ansible 59 Jul 19 21:10 lib drwxr-xr-x. 3 ansible ansible 16 Jul 19 21:10 share drwxr-xr-x. 2 ansible ansible 4096 Jul 19 21:10 bin
Now,check the new python version 2.7.6
[root@ansible ~]$ cd python/bin/ [root@ansible bin]$ python -V Python 2.7.6 [root@ansible bin]# which python /home/ansible/bin/python
Step 5:- Download PIP package
[root@ansible ~]$ curl "https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py" -o "get-pip.py" % Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0 100 1603k 100 1603k 0 0 164k 0 0:00:09 0:00:09 --:--:-- 222k [root@ansible ansible]# python get-pip.py Collecting pip Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/0f/74/ecd13431bcc456ed390b44c8a6e917c1820365cbebcb6a8974d1cd045ab4/pip-10.0.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (1.3MB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 1.3MB 709kB/s Collecting wheel Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/81/30/e935244ca6165187ae8be876b6316ae201b71485538ffac1d718843025a9/wheel-0.31.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (41kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 51kB 1.2MB/s Installing collected packages: pip, wheel Successfully installed pip-10.0.1 wheel-0.31.1 [root@ansible ansible]# python -m pip install cx_Oracle --upgrade Collecting cx_Oracle Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/3b/09/6b10675a6db7c7da1b8d23225f0a95b2a45248c56a1e8f711d59809278d3/cx_Oracle-6.4.1-cp27-cp27mu-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (590kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 593kB 1.2MB/s Installing collected packages: cx-Oracle Successfully installed cx-Oracle-6.4.1
Check the PIP version :-
[root@ansible ansible]# pip -V pip 10.0.1 from /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pip (python 2.7)
We need the Cx_Oracle Package for executing SQL’s , performing any task inside SQL prompt.
[root@ansible ansible]# python Python 2.7.5 (default, Sep 5 2016, 02:30:38) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-9)] on linux2 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> import cx_Oracle >>> exit()
Installation of Ansible software :-
Step 6:-To get Ansible for Linux, first ensure that the RHEL7 EPEL repository is installed:
[root@ansible ~]# rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm Retrieving https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm warning: /var/tmp/rpm-tmp.dwLJVq: Header V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID 352c64e5: NOKEY Preparing... ################################# [100%] Updating / installing... 1:epel-release-7-11 ################################# [100%]
Step 7:- Once the repository is installed, install Ansible with yum:
[root@ansible ~]# yum install ansible
Step 8:- Check the ansible version and configuration file path
[root@ansible ~]$ ansible --version ansible 2.6.1 config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg configured module search path = [u'/home/ansible/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules'] ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible executable location = /bin/ansible python version = 2.7.5 (default, Sep 5 2016, 02:30:38) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-9)]
Step 9:- Configuring ansible hosts and create inventory file.
The ‘database–servers‘ in the brackets indicates as group names to list number of remote hosts.
[root@ansible ~]# vi /etc/ansible/hosts
Added the below remote host entry to the /etc/ansible/hosts file
[database-servers] demo.localdomain.com
Step 10:- List the remote hosts which are able to use ansible commands
[root@ansible ~]$ ansible --list-host all hosts (1): 192.168.86.141 [ansible@ansible ~]$ ansible --list-host database-servers hosts (1): 192.168.86.141
SSH Key creation :-
Step 11:- Create the SSH user equivalence in the ansible server.
[ansible@ansible ~]$ ssh-keygen -t rsa Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/ansible/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/ansible/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /home/ansible/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: 3f:58:1b:ca:6c:2a:66:0d:63:ea:c3:18:a3:45:45:43 ansible@ansible.localdomain.com The key's randomart image is: +--[ RSA 2048]----+ | oE | | .. | | . | | . | | . S o | |o . + o = o | |.* o + * + | |o + + .o . | | ..+ .. | +-----------------+ [ansible@ansible ~]$ cd .ssh/ [ansible@ansible .ssh]$ ls -lrt total 8 -rw-r--r--. 1 ansible ansible 413 Jul 20 19:40 id_rsa.pub -rw-------. 1 ansible ansible 1675 Jul 20 19:40 id_rsa
Step 12:- Copy the SSH key to the remote servers
[root@ansible .ssh]# ssh-copy-id root@demo.localdomain.com /bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed /bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys root@demo.localdomain.com's password: Number of key(s) added: 1 Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@demo.localdomain.com'" and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
Step 13:- Now,we are able to ping the remote hosts,
[root@ansible .ssh]# ansible all -m ping
demo.localdomain.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
Step 14 :- To check the partitions on all remote hosts
[root@ansible ~]# ansible -m command -a "df -h" database-servers demo.localdomain.com | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/vg_rac1-lv_root 36G 19G 16G 55% / tmpfs 2.0G 276K 2.0G 1% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 485M 82M 378M 18% /boot