In this session , I’ll cover below topics following by some assessments
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators (1/2)
- Bit-wise Operators
- Decimal Conversions
1.Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used with numeric values to perform common mathematical operations:
- + : Add
- – : Sub
- * : Mul
- / : Div (FP)
- % : Mod
- ** : Exp
- // : Floor Div (Z)
In details , on below …
| Operator | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | x + y |
| – | Subtraction | x – y |
| * | Multiplication | x * y |
| / | Division | x / y |
| % | Modulus | x % y(remainder of x/y) |
| ** | Exponentiation | x ** y(x to the power y) |
| // | Floor division | x // y |
Example 1: Arithmetic operators in Python
Input ,

Output ,

2.Assignment operators
Assignment operators are used in Python to assign values to variables.
a = 5 is a simple assignment operator that assigns the value 5 on the right to the variable a on the left.
There are various compound operators in Python like a += 5 that adds to the variable and later assigns the same. It is equivalent to a = a + 5.
| Operator | Example | Equivalent to |
|---|---|---|
| = | x = 5 | x = 5 |
| += | x += 5 | x = x + 5 |
| -= | x -= 5 | x = x – 5 |
| *= | x *= 5 | x = x * 5 |
| /= | x /= 5 | x = x / 5 |
| %= | x %= 5 | x = x % 5 |
| //= | x //= 5 | x = x // 5 |
| **= | x **= 5 | x = x ** 5 |
| &= | x &= 5 | x = x & 5 |
| |= | x |= 5 | x = x | 5 |
| ^= | x ^= 5 | x = x ^ 5 |
| >>= | x >>= 5 | x = x >> 5 |
| <<= | x <<= 5 | x = x << 5 |
3.Bit-wise operators
Bitwise operators act on operands as if they were strings of binary digits. They operate bit by bit, hence the name.
For example, x=3 (0000 0011) in binary and y=2 (0000 0010) . and let me explain how it works in back end.
| Operator | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| & | Bitwise AND | x & y = 0 (0000 0000) |
| | | Bitwise OR | x | y = 14 (0000 1110) |
| ~ | Bitwise NOT | ~x = -11 (1111 0101) |
| ^ | Bitwise XOR | x ^ y = 14 (0000 1110) |
| >> | Bitwise right shift | x >> 2 = 2 (0000 0010) |
| << | Bitwise left shift | x << 2 = 40 (0010 1000) |
A)Bitwise AND
Python bitwise and operator returns 1 if both the bits are 1, otherwise 0.
Example , input
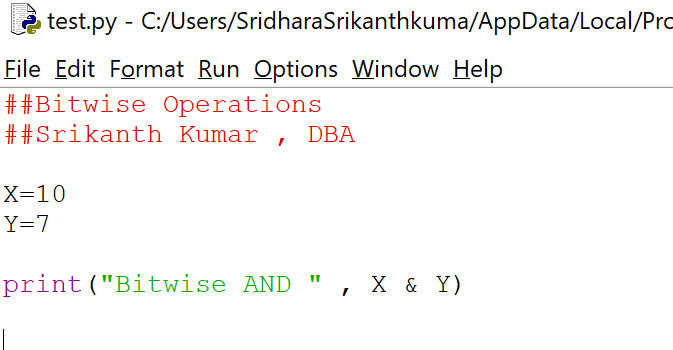
And the results is 2
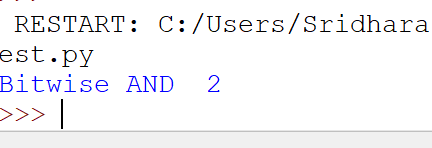
in detail ,
10 = 0000 1010 (0000 23 0 21 0) — in binary format
7 = 0000 0111(0000 0 22 21 20) — in binary format
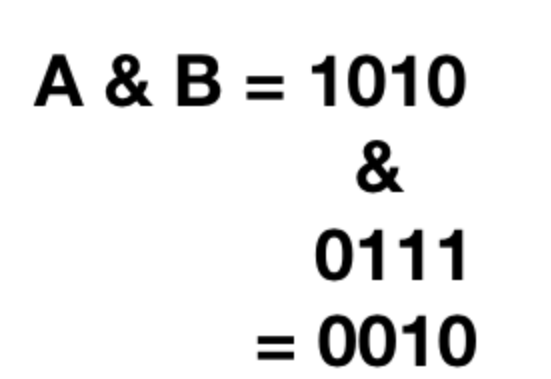
And the answer is 0010 which is 0021 0
B)Bitwise OR
Python bitwise or operator returns 1 if any of the bits is 1. If both the bits are 0, then it returns 0.

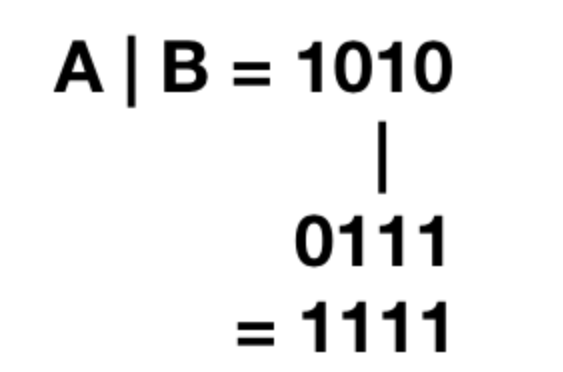
and final answer for this is , 1111 (23222120) i.e 15
C)Bitwise XOR :(^)
Python bitwise XOR operator returns 1 if one of the bits is 0 and the other bit is 1. If both the bits are 0 or 1, then it returns 0.


and the answer is 13
D)Bitwise NOT /Bitwise ones’ Complement (~)
Python Ones’ complement of a number ‘A’ is equal to -(A+1)

How it works ?
A=10=>1010
~A =~1010 =-(1010+1) =-(1011) =-11
E)Bit-wise Left shift Operator (<<)
Python bitwise left shift operator shifts the left operand bits towards the left side for the given number of times in the right operand. In simple terms, the binary number is appended with 0s at the end.
Example ,

A=10 ==>1010(Binary)
A<<2=1010<<2 ==>101000 ==>40
F) Bitwise Right Shift Operator (>>)
Python right shift operator is exactly the opposite of the left shift operator. Then left side operand bits are moved towards the right side for the given number of times. In simple terms, the right side bits are removed.
>>> 10 >> 2 2 >>>
A=10 ==>1010(Binary)
A>>2=1010>>2 ==>0010 ==>2
4.Decimal Conversions
- Bin.. bin(val/var) ==> 2 ==> 0b……
- Oct.. oct(val/var) ==> 8 ==> 0o…….
- Hex.. hex(val/var) ==>16 ==> 0x…..