NoSQL databases and management systems are the current buzzwords in the storage industry. Big data explosion is the main catalyst behind the growth and popularity of NoSQL databases. Traditional (DBMSs) are mainly designed for structured data with predefined schema. So, the relational model (RDBMS) finds it very difficult to deal with semi-structured, unstructured or other forms of data, popularly known as big data.
NoSQL – A New Way of Thinking About Databases

Before the explosion of big data, we were quite comfortable with the relational storage model, because the input data was almost in structured form. And, for the small amount of unstructured data, some mechanisms or ETL tools were used to make it structured and then load into the RDBMS. So, we never faced the challenges of managing huge volumes of unstructured data (big data).
Here’s where the role of NoSQL technology comes in. The term NoSQL originally referred to “non-relational.” NoSQL is a new way of thinking about databases and their management systems. It provides a mechanism to store and retrieve data, modeled in a non-relational way (without tabular relation). There are different types of NoSQL databases available in the market, each suitable for specific use cases. But the fundamental purpose of all these types are similar – to store semi-structured, unstructured or other forms of data.
What are NoSQL Database Management Systems?
In simple terms, NoSQL DBMS is a group of system software/libraries to manage, operate and administer non-relational databases. NoSQL database management systems are specifically designed to manage unstructured data and they are characterized by a schema-less model, high performance, scalability, distributed storage, cloud enablement, etc.
We know that unstructured data, more specifically big data, has four dimensions – volume, velocity, variety and complexity. Now, if we do a combination of these different dimensions, we get different types of data models. So, the NoSQL DBMSs are also designed to have multiple operational models based on the data and target functionality.
There are mainly four types of NoSQL DBMSs. Let us take a look at them one by one.
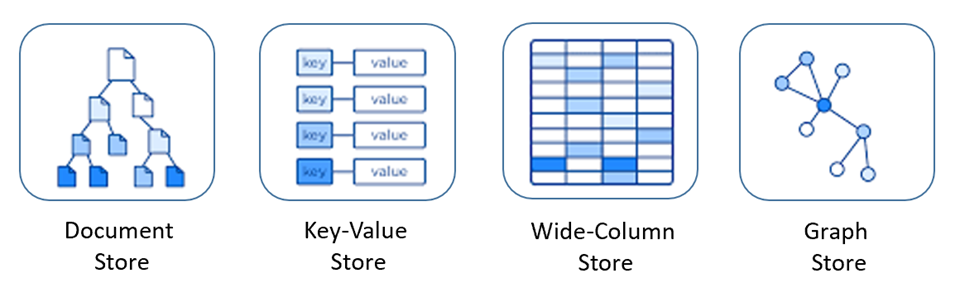
Document-Based Model :-
- Brief description: A document-based model is nothing but a key-value store, where the document is stored in the value part and retrieved by the associated key. These documents can be XML, JSON or in any other form, having a hierarchical and self-defining structure.
- When suitable: It is suitable for storing nested information, CMSs, web-based and real-time analytics, e-commerce applications, etc.
- When not suitable: It is not suitable for complex operations spreading across multiple documents or complex queries.
Key-Value-Based Model :-
- Brief description: Key-value-based NoSQL storage is the most basic type of NoSQL implementation. The journey of NoSQL DBMS started with key-value pairs only, so they are the basic backbone of the non-relational model. The value of any data is stored with a matching key without any structure or relation. And, the data is also fetched with the help of the key. It has high performance with easy scalability support.
- When suitable: The key-value model is suitable for storing basic information like user profiles, user sessions, shopping cart data, queuing and live information, etc.
- When not suitable: These are not recommended in situations where we need to perform data-based query, multiple key-based operations or relationship-based fetching, etc.
Column-Based Model :-
- Brief description: A column-based DBMS model stores related data in a family of columns. It can be imagined as a row with multiple columns containing related data and identified by a row key. The important point to note is that different rows can have different columns and new columns can also be added to any row at any point of time. So, it is not necessary to maintain the same columns for all the rows.
- When suitable: It is suitable for storing large volumes of unstructured and non-volatile data. These are mostly used for log aggregation, blogging platforms, etc.
- When not suitable: It is not recommended for any early stage development or cases where query pattern changes frequently.
Graph-Based Model :-
- Brief description: A graph database is a different flavor compared to the other three types of NoSQL storage. It stores entities with their relationships. Entities are known as nodes (having their own properties) and relations are known as edges. This is like a tree structure where all the nodes are connected based on their relationships.
- When suitable: Graph databases are suitable in scenarios where we have data with strong relationships. Some of the implementations are social networks, recommendation engines, geospatial data, etc.
- When not suitable: It is not suitable in situations where the data model does not have strong relationships among the entities. Because the success of the graph is mainly dependent on the relationship-based model.
Now we have a clear understanding of different NoSQL DBMSs and their usage. So let’s have a look on below in detail
| Consider a NoSQL datastore when ?? | Consider a relational database when ?? |
|---|---|
| You have high volume workloads that require large scale | Your workload volume is consistent and requires medium to large scale |
| Your workloads don’t require ACID guarantees | ACID guarantees are required |
| Your data is dynamic and frequently changes | Your data is predictable and highly structured |
| Data can be expressed without relationships | Data is best expressed relationally |
| You need fast writes and write safety isn’t critical | Write safety is a requirement |
| Data retrieval is simple and tends to be flat | You work with complex queries and reports |
| Your data requires a wide geographic distribution | Your users are more centralized |
| Your application will be deployed to commodity hardware, such as with public clouds | Your application will be deployed to large, high-end hardware |